Osteosarcoma is a cancer of the bones. It occurs when the cells in the bone begin to divide abnormally. Although it mostly affects the bones, it may also affect soft tissues. This is rare cancer and can be treated if diagnosed at an early stage.
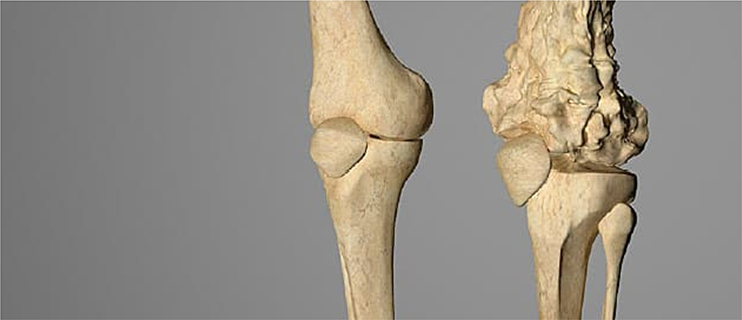
The early symptoms of osteosarcoma are pain and tenderness in the bones. The symptoms, however, aggravate as cancer begins to proliferate. The common symptoms include:
- Bone fracture.
- Fever.
- Extreme fatigue.
- Redness at the tumour site.
- Presence of lumps.
- Abrupt weight loss.
- Mobility issues.
- Anaemia.
The exact cause of osteosarcoma is not known. The possible causes, however, include:
- Age.
- Family history.
- Existing bone disorder.
- Genetic disorder.
Osteosarcoma is diagnosed by:
- Physical examination: The doctor will assess the medical condition by checking for lumps, fractures, or redness. The doctor may also ask about your medical history to understand the overall health condition.
- Imaging tests: Various imaging tests such as CT scans, and MRIs will be performed to gauge the size, location, and stage of the tumour.
- Biopsy: The doctor will extract a small tissue from the area and examine for the presence of cancer cells.
- Bone scan: The doctor will also conduct a bone scan to examine the tumour inside the bones.
The treatment strategy for osteosarcoma depends on the stage and type of cancer, age, and overall health of the patient. Surgery is usually the mainstay of the treatment. It may be combined with chemotherapy and radiation therapy for better outcomes.
- Surgery: Surgery is the mainstay of osteosarcoma. The doctor will remove the tumour in a way to reduces disability. In advanced stages, amputation may be needed to prevent cancer from spreading.
- Radiation therapy: High energy X-rays will be used to destroy cancer cells. These radiations may be administered before or after the surgery depending on the patient’s condition.
- Chemotherapy: High doses of anti-cancer drugs will be administered to destroy cancer cells. In some cases, chemotherapy is combined with radiation therapy to remove cells from the body.
- Targeted therapy: Certain drugs will also be administered to target specific cancer cells. This therapy is reserved for advanced cancer.
- Cryotherapy: During this procedure, liquid nitrogen will be administered to freeze and kill tumour cells


